Terminology
Electoral Process Terminology
An Election refers to a process where one particular office is elected. Based on this definition, the election of the President of country X and the election of Governor of province Y are, in fact, two different elections. In this same sense, a Referendum describes a process where a particular question or proposition, along with the possible answers (options), is posed to the voters.
An Electoral event corresponds to any given event on which one or more elections or referenda take place. It also applies to events that combine both.
An Electoral authority refers to the body that manages the electoral event. This authority can be single and centralized or it can have subordinate authorities that manage specific jurisdictions within the country.
On every electoral event voting instruments (such as ballots, voters lists and count templates) are generated for each polling station, these voting instruments are consolidated in a single package for delivery to each polling location, this package is called an electoral kit. A polling station is a place, within a polling location, where citizens go to vote. One polling location (such as a school) can have more than one polling station. Each polling station has designated poll workers who act as election officials at that level.
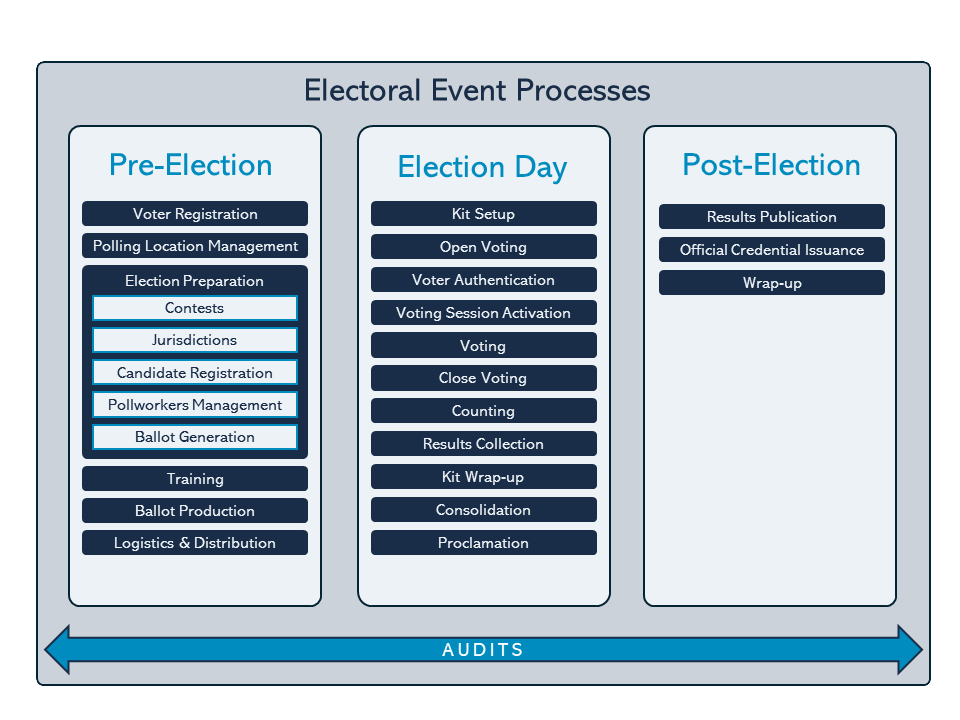
Many different processes need to take place for the successful completion of an Electoral event. Figure 1 illustrates those activities and a sequence of execution that fits more electoral events today, no matter whether they are conducted completely manually or with any sort of technological assistance. The following table provides a brief description of each process.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Voter registration | Is the process where citizens register to vote. This process can happen continuously or it can be activated a couple of months before the electoral event. |
| Polling location management | The process of identifying, assessing and preparing the polling locations for the electoral event. |
| Election preparation | This process entails all the activities required to prepare all the voting instruments used during the election. It’s main internal activities include: Gathering the information of all the contests (offices or propositions) and the geo-political jurisdictions those contests apply to. Candidate registration: the process whereby candidates can register in order to run for a specific office. Poll worker management: the process where the poll workers are selected and managed. Ballot generation: entails the generation of all the instruments required for the electoral event. This includes not only the ballots where the voter selects his/her preferred options but also all materials needed to conduct the election such as: voters lists, count forms, indelible ink, among others. IMPORTANT NOTE: the ballot generation process refers strictly to the generation of the instruments in their logical form. The mass printing of ballots and the other instruments is part of the Ballot production process that will be defined later. Platform readiness: refers to the process that certifies that the entire electoral infrastructure is ready for the electoral event. This part of the process can include the completion of field tests and even mock elections. |
| Training | This process refers to the preparation and training of all the actors of the electoral infrastructure, such as: Voters Poll workers Support specialists Warehouse operators Consolidation operators |
| Ballot production | This process encompasses the actual production of all voting instruments as well as their preparation and packaging into electoral kits. Some of the activities performed are: Ballot printing, Forms printing (counting, consolidation forms) Ballot box production Electoral kit preparation |
| Logistics & distribution | The process of delivering the electoral kits to each polling location either directly or using intermediate distribution sites. |
| Kit setup | The process of receiving, verifying and organizing the Electoral Kit into the polling station. |
| Open Voting | This process encompasses the act of allow entry of voters to polling station to exercise their right to vote |
| Voter authentication | The following 3 processes refer to the direct interactions that each voter has with the electoral event at the polling station. Starting with voter authentication where the poll workers verify the identity of each voter as well as validate whether they are entitled to vote. |
| Voting session activation | The session activation refers specifically to the action where the poll worker enables the voter to vote by handing him or her, the voting instrument. |
| Voting | The main process of all electoral events, VOTING refers to the activity where the voter selects his or her preferred options on the voting instrument and then casts the vote by placing the ballot in a ballot box. |
| Close voting | This process encompasses the act of close the polling station. Voters are not allowed to vote after this process. |
| Counting | Once the end of the voting hours has been reached, counting is the process whereby the poll workers open the ballot box and start the validation and counting of each and every ballot cast. This process usually ends with the preparation and filing of a counting form (per polling station) that is then delivered to a consolidation center. |
| Results collection | The process of delivering the polling station counts to a consolidation center that can be centralized or distributed throughout the country. |
| Kit wrap-up | Collection of the electoral kit, results report and any other electoral material. |
| Consolidation | Consolidation deals with aggregating the counts that are coming from the different polling stations into a repository where final results can be calculated. |
| Proclamation | Once all results are consolidated, the Proclamation is the process where the algorithms required to determine the winners from the votes are applied. |
| Result Publication | Web publication of the election results |
| Official credential issuance | As its name states, this process refers to the production and delivery of the formal proclamation document to each winner. |
| Results publication | Publication of results for the general audience, either by printed media or the internet. |
| Wrap-up | Collection and consolidation of electoral kits from the polling locations back to a centralized warehouse. |